The Entertainment Model is a theory that explains how media content is created to entertain and engage audiences, rather than to inform or educate. This model is widely used in media studies and has been the subject of both praise and criticism. In this essay, we will discuss the Entertainment Model, its criticisms, and provide relevant citations and references.
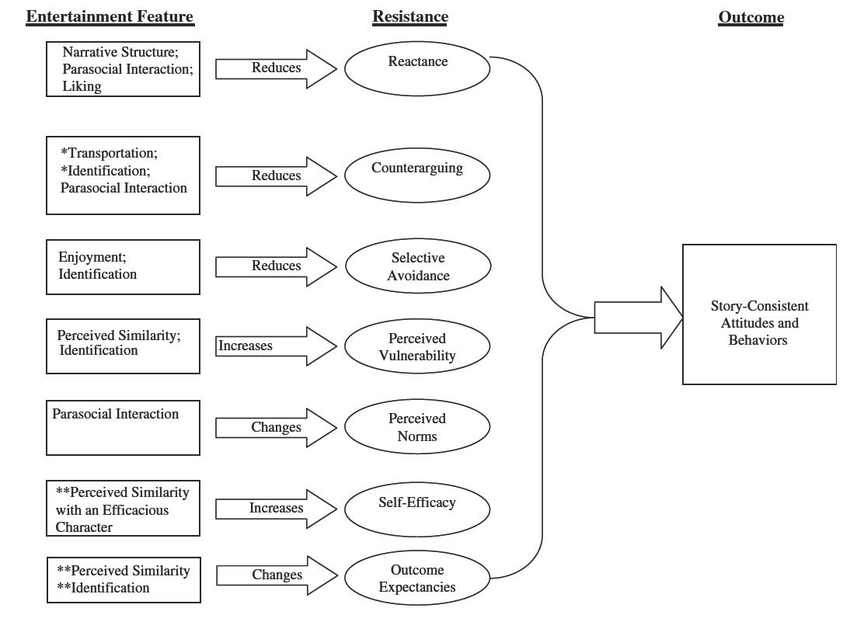
The Entertainment Model suggests that media content is primarily created to attract and retain audiences. This model is often used in the entertainment industry, including television shows, movies, music, and video games. Proponents of this theory argue that the primary goal of media producers is to create content that is engaging and enjoyable for viewers or listeners. According to this theory, the content of the media does not have to be informative or educational to be successful.
Critics of the Entertainment Model argue that it encourages the production of shallow, meaningless content that is focused solely on profit, rather than on the needs and interests of the audience. Some critics also argue that the model can lead to the creation of content that is inappropriate or offensive, as producers may be more concerned with gaining attention and boosting their ratings or revenue than with producing high-quality content.
One example of the Entertainment Model in action is the reality television genre, which often focuses on entertaining viewers with drama, conflict, and spectacle, rather than providing any meaningful educational or informative content. Proponents of the Entertainment Model might argue that these shows are popular precisely because they provide an engaging form of entertainment that many viewers enjoy.
However, critics of the Entertainment Model argue that reality television can be harmful, as it often portrays negative stereotypes and reinforces harmful social attitudes. For example, reality TV shows that focus on romantic relationships may promote unrealistic and unhealthy relationship dynamics, while shows that focus on competitions or survival may promote an unhealthy focus on winning at all costs.
In conclusion, while the Entertainment Model has its supporters, it also has its critics. Critics argue that the model encourages the production of shallow, meaningless content, while supporters argue that it simply reflects the interests and desires of audiences. Ultimately, whether or not the Entertainment Model is a valid and useful framework for media studies is a matter of ongoing debate and discussion.
References:
Gripsrud, J. (2000). The Dynasty Years: Hollywood Television and Critical Media Studies. Routledge.
Livingstone, S. (2009). On the mediation of everything: ICA presidential address 2008. Journal of communication, 59(1), 1-18.
Miller, T., & McAllister, M. P. (2001). Digital content and the cultural industries. Information Society, 17(3), 147-158.
Turow, J. (2011). The entertainment divide: how the media shape our perceptions of reality. Oxford University Press
