As a media student, you are likely to come across two primary research methods: inductive and deductive research. Both approaches are important in the field of media research and have their own unique advantages and disadvantages. In this essay, we will explore these two methods of research, along with some examples to help you understand the differences between the two.
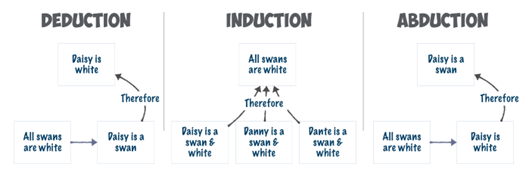
Inductive research is a type of research that involves starting with specific observations or data and then moving to broader generalizations and theories (Theories, Models and Concepts) It is a bottom-up approach to research that focuses on identifying patterns and themes in the data to draw conclusions. Inductive research is useful when the research problem is new, and there is no existing theoretical framework to guide the study. This method is commonly used in qualitative research methods like ethnography, case studies, and grounded theory.
An example of inductive research in media studies would be a study of how social media has changed the way people interact with news. The researcher would start by collecting data from social media platforms and observing how people engage with news content. From this data, the researcher could identify patterns and themes, such as the rise of fake news or the tendency for people to rely on social media as their primary news source. Based on these observations, the researcher could then develop a theory about how social media has transformed the way people consume and interact with news.
On the other hand, deductive research involves starting with a theory or hypothesis (Developing a Hypothesis: A Guide for Researchers) and then testing it through observations and data. It is a top-down approach to research that begins with a general theory and seeks to prove or disprove it through empirical evidence. Deductive research is useful when there is an existing theory or hypothesis to guide the study. This method is commonly used in quantitative research methods like surveys and experiments.
An example of deductive research in media studies would be a study of the impact of violent media on aggression. The researcher would start with a theory that exposure to violent media leads to an increase in aggressive behavior. The researcher would then test this theory through observations, such as measuring the aggression of participants who have been exposed to violent media versus those who have not. Based on the results of the study, the researcher could either confirm or reject the theory.
Both inductive and deductive research are important in the field of media studies. Inductive research is useful when there is no existing theoretical framework, and the research problem is new. Deductive research is useful when there is an existing theory or hypothesis to guide the study. By understanding the differences between these two methods of research and their applications, you can choose the most appropriate research method for your media research project.
